文章编号: 2096-3203(2021)06-0121-06 中图分类号: TM773
2. 中国矿业大学电气与动力工程学院, 江苏 徐州 221116
为解决当前日益严重的能源危机,分布式光伏、风电及储能等分布式电源(distributed generation, DG)接入配电网的比例越来越高。DG接入配电网对升级能源结构、改善网络运行经济性和提高供电可靠性等有积极的推动作用[1-3]。但伴随着DG的接入,配电网结构由传统简单的单电源放射状网络变为复杂的多电源网络,传统的三段式电流保护策略面临无法克服的选择性问题[4]。根据国家2010年颁布出台的《分布式电源接入电网技术规定》[5]和IEEE发布的《IEEE 1547-2003》标准[6],当含DG配电网发生故障时,要求保护装置迅速隔离相关DG。传统的保护策略不仅无法充分发挥DG配电网的支撑作用,而且严重限制了新能源技术的推广与应用。面对含DG配电网保护存在的诸多问题,研究新的保护方案迫在眉睫。
解决含DG配电网线路保护问题最有效的方案是纵联保护方案,但当前配电网的智能化水平和通信条件无法满足纵联保护对数据的高同步要求。当前含DG配电网保护方案主要为:利用部分故障分量进行故障识别, 主要利用所有故障类型均包含的正序故障分量, 使用其所含的电流幅值及相位信息设定差动保护判据[7-9],但未从根本上解决同步性难题,若进行相应智能化改造将带来极大的
基础建设成本;使用故障自同步时间信息构造的差动保护判据,解决了配电网环境下的同步问题[10],但对信息传递的准确性要求较高;采用零序分量改进的接地距离保护[11-14]、利用电流比幅值构造的纵联保护方案,针对不同的馈线结构,给出了适应性保护动作判据,其实现同样需装配智能配电终端平台[15-17],不符合配电网应用现状。因此,将纵联保护策略应用于含DG配电网应解决的主要问题是如何在现有弱同步条件下实现电流同步相位信息获取,同时保证保护动作的选择性和灵敏性[18-22]。
文中针对含DG配电网自动化水平较低、难以获取电流同步相位信息的难题,提出了故障信息自同步技术。通过此技术测算得到的时间信息可计算被保护线路两侧电流相位变化方向的判定值,有效代替了同步采样环节。基于故障信息自同步技术,文中提出了含DG配电网弱同步条件下的新型纵联保护方案,仅需要比较故障后工频基波电流相位变化方向判定值,即可实现纵联保护可靠动作。仿真结果表明,故障信息自同步技术具有较高的准确性,新型纵联保护方案可准确识别故障位置,对区内故障可快速、灵敏动作,对区外故障可靠制动。
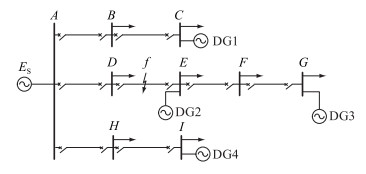
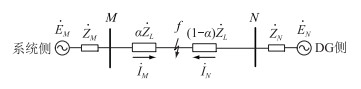
1 含DG配电网电流方向变化特性分析DG接入配电网后,配网结构变为多电源网络,如图 1所示,等效双机系统模型如图 2所示,其中系统电源等效为ES, 相应节点所带负荷由箭头表示。
|
图 1 含DG配电网结构示意 Fig. 1 Distribution network structure diagram with DG |
|
图 2 含DG配电网等效网络模型 Fig. 2 Equivalent network model with DG distribution network |
图 2中,ĖM为系统侧等效电势;ĖN为DG侧等效电势;ŻM为系统侧等效阻抗;ŻN为DG侧等效阻抗;ŻL为线路MN的阻抗值; α为故障点距离系统侧的距离占线路总长的比值;İM,İN分别为被保护线路两侧电流相量。
1.1 区内故障电流方向变化特性含DG配电网正常运行时,设定电流由母线流向线路为正方向,根据图 2可知,正常运行电流为:
| $ {\dot I_M} = - {\dot I_N} = \frac{{{{\dot U}_M} - {{\dot U}_N}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L}}} $ | (1) |
式中:
设定系统运行在正常方式下,忽略线路电阻,若被保护线路MN阻抗角与两端电源的阻抗角相同,当距系统侧αŻL处发生故障时,可以将线路两侧故障电流等效为网络正常运行状态下的电流与故障分量的叠加,即:
| $ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{\dot I'}_M} = {{\dot I}_M} + {{\dot I}_{fM}}}\\ {{{\dot I'}_N} = {{\dot I}_N} + {{\dot I}_{fN}}} \end{array}} \right. $ | (2) |
式中:İ ′ M,İ ′ N分别为故障后被保护线路两侧电流相量;İfM,İfN分别为故障后被保护线路两侧故障电流分量。
设系统正常运行时故障点电压为
| $ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{L}} {{{\dot I}_{fM}} = - \frac{{ - {{\dot U}_f}}}{{\alpha {{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}} = \frac{{{{\dot U}_f}}}{{\alpha {{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}}}\\ {{{\dot I}_{fN}} = - \frac{{ - {{\dot U}_f}}}{{\left( {1 - \alpha } \right){{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}} = \frac{{{{\dot U}_f}}}{{\left( {1 - \alpha } \right){{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}}} \end{array}} \right. $ | (3) |
则故障后线路两侧电流为:
| $ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{L}} {{{\dot I'}_{fM}} = \frac{{{{\dot U}_M} - {{\dot U}_N}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L}}} + \frac{{{{\dot U}_f}}}{{\alpha {{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}}}\\ {{{\dot I'}_N} = - \frac{{{{\dot U}_M} - {{\dot U}_N}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L}}} + \frac{{{{\dot U}_f}}}{{\left( {1 - \alpha } \right){{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_N}}}} \end{array}} \right. $ | (4) |
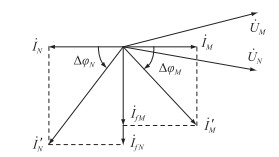
相应电压、电流相量关系如图 3所示。
|
图 3 区内故障电流相量变化图 Fig. 3 The phasor variation diagram of fault current in the zone |
由图 3可知,故障前线路两侧电流İM,İN大小相同,方向相反。故障发生后,流过M端的电流相位变化ΔφM < 0°,其电流相位变化方向为负;流过N端的电流相位变化ΔφN>0°,其电流相位变化方向为正。
1.2 区外故障电流方向变化特性若在线路区外靠近N端处发生故障时,流过线路两侧的故障电流为:
| $ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{l}} {{{\dot I}_{fM}} = - \frac{{ - {{\dot U}_f}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}} = \frac{{{{\dot U}_f}}}{{\alpha {{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}}}\\ {{{\dot I}_{fN}} = \frac{{ - {{\dot U}_f}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}} = - \frac{{{{\dot U}_f}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}}} \end{array}} \right. $ | (5) |
则可得故障后线路两侧电流为:
| $ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{L}} {{{\dot I'}_M} = \frac{{{{\dot U}_M} - {{\dot U}_N}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L}}} + \frac{{{{\dot U}_f}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}}}\\ {{{\dot I'}_N} = - \left( {\frac{{{{\dot U}_M} - {{\dot U}_N}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L}}} + \frac{{{{\dot U}_f}}}{{{{\dot Z}_L} + {{\dot Z}_M}}}} \right)} \end{array}} \right. $ | (6) |
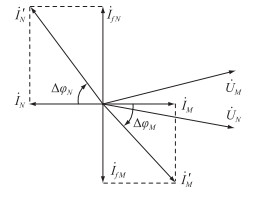
相应电压、电流相量关系如图 4所示。
|
图 4 区外故障电流相量变化图 Fig. 4 Out-of-area fault current phasor variation diagram |
由图 4可知,故障前线路两侧电流İM,İN大小相同,方向相反。故障发生后,流过M端的电流相位变化ΔφM < 0°,其电流相位变化方向为负;流过N端的电流相位变化ΔφN < 0°,其电流相位变化方向为负。
当故障点在故障区外靠近M点时,电流相位变化特性与靠近N点区外故障类似,但其电流向量变化方向均为正。
2 有源配电网环境下的故障信息自同步技术 2.1 故障信息自同步技术原理在配电网无法实现两侧同步对时的情况下,文中提出了故障信息自同步技术,基本原理为:配电线路容抗要远大于输电线路阻抗,对地电容电流对线路电流相位变化影响极小,因此,故障发生前被保护线路两端基波电流相位相差180°,即线路两端基波电流波形峰值点间隔半个周期,两相邻相同趋势峰值点间隔一个周期。对于被保护线路两端,故障是同时发生的。以故障发生时刻为时间参考点,分别测量线路两侧工频基波电流故障时刻前后两相邻相同趋势峰值点的时间间隔。通过此时间间隔计算得到线路两侧电流变化方向,即可替代同步采样环节。故障同步识别技术实现原理见图 5。
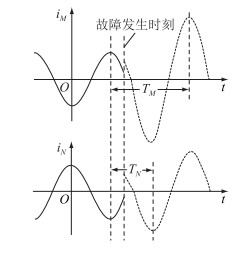
|
图 5 故障信息自同步技术原理 Fig. 5 Schematic diagram of fault information self-synchronization technology |
图 5中,两侧基波电流故障时刻前后两相邻相同趋势峰值点的时间间隔分别为TM,TN,根据时间信号可得故障后线路两端电流相位变化量为:
| $ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\Delta {\varphi _M} = \frac{{{T_M} - T}}{T} \times 2{\rm{ \mathit{ π} }}}\\ {\Delta {\varphi _N} = \frac{{{T_N} - T}}{T} \times 2{\rm{ \mathit{ π} }}} \end{array}} \right. $ | (7) |
式中:T为工频基波电流信号周期。T取0.02 s,则式(7)变化为:
| $ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\Delta {\varphi _M} = 100{\rm{ \mathit{ π} }} \times {\mathit{T}_M} - 2{\rm{ \mathit{ π} }}}\\ {\Delta {\varphi _N} = 100{\rm{ \mathit{ π} }} \times {\mathit{T}_N} - 2{\rm{ \mathit{ π} }}} \end{array}} \right. $ | (8) |
通过上述故障信息自同步技术可以很好地克服配电网无法获取同步信息的困难,为新型纵联保护方案应用提供了数据信息支持。
2.2 峰值点计算与误差分析电流采样数据均为正弦波上的值,正弦波在峰值点斜率为0,则电流峰值点前一个采样点的采样值变化斜率为正,在电流峰值点后一个采样点的采样值变化斜率为负。根据峰值点前后采样值变化斜率异号的特性,可通过对峰值点前后2个采样点进行线性拟合来计算得到峰值点。
设定在Tk时刻对应的采样值为Dk,则峰值点前后2个采样点Tk-1,Tk,Tk+1,Tk+2时刻对应的电流采样值分别为Dk-1,Dk,Dk+1,Dk+2。通过采样值线性拟合,使用线性插值法可得峰值点时刻为:
| $ {T_{{\rm{MAX}}}} = {T_k} + \frac{{\left( {{T_{k + 1}} - {T_k}} \right)\left( {{D_{k + 2}} - {D_{k + 1}}} \right)}}{{{D_{k + 2}} + {D_k} - {D_{k + 1}} - {D_{k - 1}}}} $ | (9) |
若系统采样周期为TS,计算峰值点产生的误差小于TS/2,在计算基波电流相位变化时产生的误差也很小。系统采样频率越高,电流峰值点计算精度越高,故障信息自同步技术识别精度越高,所以应在装置允许条件下提高采样频率。
3 新型有源配电网纵联保护方案根据基尔霍夫电流定律,含DG配电网区内、外故障时,线路两侧电流相位变化特性不同,可得新型纵联保护原理为:
(1) 当线路发生区内故障时,线路两侧电流相位变化方向相反;
(2) 当线路发生区外故障时,线路两侧电流相位变化方向相同。
根据新型含DG配电网纵联保护原理,只需使用故障信息自同步技术测取线路两侧电流相量变化方向,即可判定故障位置。若故障发生在被保护线路内部,则保护动作将被保护线路从系统中切除;若故障发生在线路区外则保护不动作。
设定基波电流变化方向为正时判定值为1;基波电流变化方向为负时判定值为-1;若未识别出变化则判定值为0。当两节点电流变化方向判定值异号时即可判定其区内发生故障。
文中提出了故障位置判定表来完成故障位置判定。以图 1所示的含DG配电网为例,若EF范围内发生故障,基于故障信息自同步技术可得判定表,如表 1所示。
|
|
表 1 基于故障信息自同步技术的故障位置判定 Table 1 Fault location determination based on fault information self-synchronization technology |
其中,Ti为含DG网络中各节点基波电流故障时刻前后两相邻相同趋势峰值点的时间间隔;Δφi为根据故障信息自同步技术得到相应节点的基波电流的相位变化量。由故障位置判定表,判定值在EF两相邻节点为异号,其他相邻节点判定值均为同号,即可判定故障发生在EF范围内。EF线路两侧保护动作,即可靠切除故障。保护方案逻辑如图 6所示,图中线路流变用CT表示。
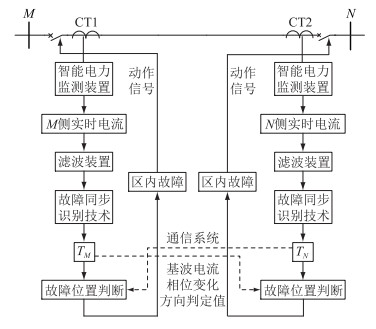
|
图 6 保护方案逻辑 Fig. 6 Protection scheme logical diagram |
为验证故障信息自同步技术的准确性和纵联保护方案的有效性,文中利用Matlab/Simulink仿真平台搭建200 MV ·A的10 kV含DG配电网模型。配电网模型中逆变型DG(inverter interfaced DG,IIDG)采用PQ控制策略,有功、无功出力值分别为4.73 MW,2.30 Mvar。DG接入容量均为国家标准允许最大值的25%。带有负荷的节点负荷均设定为5.40 MW,功率因数为0.85。
线路AB,AD,AH,DE为架空线路,单位线路参数为0.17+j0.38 Ω/km,线路BC,EF,FG,HI为电缆线路,单位线路参数为0.035+j0.088 Ω/km,线路长度如图 7所示。
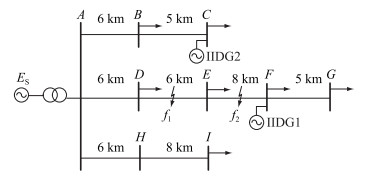
|
图 7 含DG配电网仿真模型 Fig. 7 Distribution network simulation model with DG |
首先,文中仿真了线路DE距D端50%处发生三相金属性接地故障,分别记录含DG网络中各节点基波电流故障时刻前后两相邻相同趋势峰值点的时间间隔Ti,并根据故障信息自同步技术得到相应节点的基波电流相位变化量Δφi。其中以a相基波电流Ia为例,线路DE两端电流变化如图 8所示,DE节点电流相位变化信息如表 2所示。
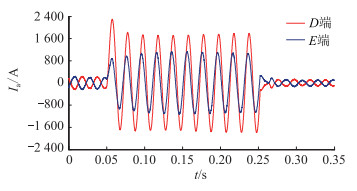
|
图 8 线路DE区内发生三相短路时两端电流变化波形 Fig. 8 Waveforms of current variation at both ends when three-phase short circuit occurs in line DE |
|
|
表 2 区内故障时系统相关节点电流相位变化信息 Table 2 The current phase change information of the relevant nodes in the system during the fault |
由仿真结果可知,故障信息自同步技术可准确获得系统各节点电流相位变化方向,新型含DG配电网纵联保护方案可准确判定线路DE区内发生故障,保护动作将线路DE从系统中切除,保护具有良好的选择性和可靠性。
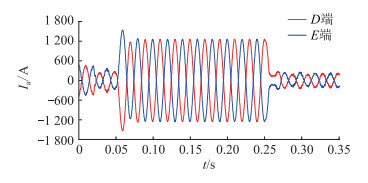
4.2 区外故障仿真分析区外故障仿真了线路EF距E端50%处发生三相金属性接地故障,分别记录含DG网络中各相关节点基波电流故障时刻前后两相邻相同趋势峰值点的Ti,并根据故障信息自同步技术得到相应节点基波电流Δφi。其中以a相基波电流Ia为例,线路DE两端电流变化如图 9所示,DE节点电流相位变化信息如表 3所示。
|
图 9 线路DE区外发生三相短路时两端电流变化波形 Fig. 9 Waveforms of current variation at both ends when three-phase short circuit occurs outside DE area |
|
|
表 3 区外故障时系统相关节点电流相位变化信息 Table 3 The current phase change information of the relevant nodes in the system in case of out-of-area fault |
当发生区外故障时,故障信息自同步技术依然可以准确获得系统各节点电流相位变化方向,新型含DG配电网纵联保护方案可准确判定线路DE区外发生故障,保护可靠不动作。
由仿真结果可以看出,故障信息自同步技术可准确识别故障并获取线路各相关节点的电流相位变化信息。当被保护线路区内发生故障时,新型含DG配电网纵联保护方案具有良好的选择性和灵敏性,可准确判定故障发生在区内并快速切除故障。当被保护线路区外发生故障时,文中提出的保护方案可实现可靠制动。
5 结语文中首先提出了适用于有源配电网的故障信息自同步技术,以两侧基波电流故障时刻前后两相邻相同趋势峰值点的时间间隔数据代替传统的电流同步相位数据,解决了当前配电网因难以获取同步采样数据导致纵联差动保护方案无法应用于有源配电网的难题。
基于故障信息自同步技术,文中提出了新型含DG配电网纵联保护方案。新型纵联保护方案只需使用故障信息自同步技术测得的电流相位变化方向判定值,即可完成故障位置判定,具有良好的选择性、灵敏性和可靠性,可在有源配电网环境下有效应用。
| [1] |
金能, 梁宇, 邢家维, 等. 提升配电网线路保护可靠性的远方保护及其与就地保护优化配合方案研究[J]. 电工技术学报, 2019, 34(24): 5221-5233. JIN Neng, LIANG Yu, XING Jiawei, et al. Research on remote protection and the optimized coordination scheme of local-remote protection to enhance the protection reliability of the line in distribution network[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2019, 34(24): 5221-5233. (  0) 0) |
| [2] |
张家安, 安世兴, 陈建, 等. 考虑分布式电源灵活接入下的配电网风险评估[J]. 供用电, 2019, 36(5): 29-33. ZHANG Jiaan, AN Shixing, CHEN Jian, et al. Distribution network risk assessment considering the flexible access of DG[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2019, 36(5): 29-33. (  0) 0) |
| [3] |
赵宇明, 丁庆, 秦毅, 等. 深圳电网分布式电源与用户侧储能技术实践与思考[J]. 供用电, 2019, 36(3): 76-82. ZHAO Yuming, DING Qing, QIN Yi, et al. Practice and reflection of distributed generation and user side energy storage in Shenzhen power grid[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2019, 36(3): 76-82. (  0) 0) |
| [4] |
张维, 宋国兵, 豆敏娜, 等. 适应分布式电源接入的双模式馈线自动化研究[J]. 供用电, 2019, 36(5): 66-71. ZHANG Wei, SONG Guobing, DOU Minna, et al. Research on dual mode feeder automation solution for distribution networks with distributed generation[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2019, 36(5): 66-71. (  0) 0) |
| [5] |
国家电网公司. 分布式电源接入电网技术规定: Q/GDW 480-2010[S]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2010. State Grid Corporation of China. Technical rule for distributed resources connected to power grid: Q/GDW 480-2010[S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2010. (  0) 0) |
| [6] |
IE EE. 1547-2003-IEEE standard for interconnecting distributed resources with electric power systems[J]. Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers Inc, 2003. (  0) 0) |
| [7] |
周成瀚, 邹贵彬, 杜肖功, 等. 基于正序电流故障分量的有源配电网纵联保护[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2020, 40(7): 2102-2112, 2390. ZHOU Chenghan, ZOU Guibin, DU Xiaogong, et al. A pilot protection method based on positive sequence fault component current for active distribution networks[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2020, 40(7): 2102-2112, 2390. (  0) 0) |
| [8] |
雷霖, 唐成达, 青禹成, 等. 含逆变型分布式电源的配电网正序综合阻抗纵联保护[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46(18): 149-155. LEI Lin, TANG Chengda, QING Yucheng, et al. Pilot protection of positive sequence component integrated impedance for distribution network with inverter interfaced distributed generator[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46(18): 149-155. DOI:10.7667/PSPC171464 (  0) 0) |
| [9] |
王艳松, 刘珊, 衣京波, 等. 基于状态估计的含分布式电源树状配电网故障测距算法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2018, 46(23): 60-67. WANG Yansong, LIU Shan, YI Jingbo, et al. Fault location algorithm based on state estimation in tree distribution network with distributed generation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2018, 46(23): 60-67. DOI:10.7667/PSPC171749 (  0) 0) |
| [10] |
李瀚霖, 陆于平, 黄涛, 等. 基于故障同步识别的含分布式电源配电网充分式差动保护[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2016, 40(11): 100-107. LI Hanlin, LU Yuping, HUANG Tao, et al. Sufficient differential protection for distribution network with distributed generators based on fault synchronous identification[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(11): 100-107. DOI:10.7500/AEPS20150403007 (  0) 0) |
| [11] |
杨晶晶, 林凡勤, 周成瀚, 等. 含分布式电源的馈线电流序分量比较式保护[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(15): 116-123. YANG Jingjing, LIN Fanqin, ZHOU Chenghan, et al. Comparison protection method of current sequence components for feeder with distributed generation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(15): 116-123. DOI:10.7667/PSPC20191516 (  0) 0) |
| [12] |
董凯达, 蔡燕春, 金震. 小电阻接地配电网零序保护的改进研究[J]. 供用电, 2020, 37(6): 48-52, 65. DONG Kaida, CAI Yanchun, JIN Zhen. The research on the improvement of the zero-sequence relay for the low resistance grounded distribution network[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2020, 37(6): 48-52, 65. (  0) 0) |
| [13] |
张兆云, 陈卫, 张哲, 等. 一种广域差动保护实现方法[J]. 电工技术学报, 2014, 29(2): 297-303. ZHANG Zhaoyun, CHEN Wei, ZHANG Zhe, et al. A method of wide-area differential protection[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2014, 29(2): 297-303. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2014.02.036 (  0) 0) |
| [14] |
武利会, 黄辉, 范心明, 等. 交直流混联配电网换流变压器零序保护优化配置[J]. 供用电, 2019, 36(10): 41-46, 79. WU Lihui, HUANG Hui, FAN Xinming, et al. Optimal configuration of zero-sequence protection for converter transformer in AC/DC hybrid distribution network[J]. Distribution & Utilization, 2019, 36(10): 41-46, 79. (  0) 0) |
| [15] |
NAIEM A F, HEGAZY Y, ABDELAZIZ A Y, et al. A classification technique for recloser-fuse coordination in distribution systems with distributed generation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2012, 27(1): 176-185. DOI:10.1109/TPWRD.2011.2170224 (  0) 0) |
| [16] |
COFFELE F, DYSKO A, BOOTH C, et al. Quantitative analysis of network protection blinding for systems incorporating distributed generation[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2012, 6(12): 1218-1224. (  0) 0) |
| [17] |
侯重远, 江汉红, 芮万智, 等. 面向交换式电力监测网的NTP同步精度提高方法[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2013, 33(1): 148-152. HOU Chongyuan, JIANG Hanhong, RUI Wanzhi, et al. Improvement of NTP synchronization accuracy for switch-oriented power monitoring networks[J]. Electric Power Automation Equipment, 2013, 33(1): 148-152. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6047.2013.01.028 (  0) 0) |
| [18] |
韦明杰, 石访, 张恒旭, 等. 基于零序电流波形区间斜率曲线的配电网高阻接地故障检测[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44(14): 164-171. WEI Mingjie, SHI Fang, ZHANG Hengxu, et al. Detection of high impedance grounding fault in distribution network based on interval slope curves of zero-sequence current[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(14): 164-171. (  0) 0) |
| [19] |
曾德辉, 王钢, 郭敬梅, 等. 含逆变型分布式电源配电网自适应电流速断保护方案[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2017, 41(12): 86-92. ZENG Dehui, WANG Gang, GUO Jingmei, et al. Adaptive current protection scheme for distribution network with inverter-interfaced distributed generators[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41(12): 86-92. DOI:10.7500/AEPS20160811002 (  0) 0) |
| [20] |
马帅, 武志刚, 高厚磊, 等. 适配高渗透率DG接入配电网的幅值比较式保护[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(4): 43-50. MA Shuai, WU Zhigang, GAO Houlei, et al. Amplitude comparison protection for distribution network with high permeability distributed generation[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(4): 43-50. (  0) 0) |
| [21] |
李娟, 高厚磊, 朱国防. 考虑逆变类分布式电源特性的有源配电网反时限电流差动保护[J]. 电工技术学报, 2016, 31(17): 74-83. LI Juan, GAO Houlei, ZHU Guofang. Inverse-time current differential protection in active distribution network considering characteristics of inverter-interfaced distributed generations[J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2016, 31(17): 74-83. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6753.2016.17.008 (  0) 0) |
| [22] |
谢民, 王同文, 徐靖东, 等. 分布式电源对配网继电保护影响及综合改进保护方案[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(19): 78-84. XIE Min, WANG Tongwen, XU Jingdong, et al. Effect of distributed generation on relay protection of distribution network and comprehensive improvement of protection scheme[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(19). (  0) 0) |
2. School of Electrical and Power Engineering, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou 221116, China
 2021, Vol. 40
2021, Vol. 40


 李瀚霖(1990), 男, 硕士, 工程师, 从事调度运行工作(E-mail:
李瀚霖(1990), 男, 硕士, 工程师, 从事调度运行工作(E-mail: