文章编号: 2096-3203(2021)01-0138-04 中图分类号: TM852 文献标识码: A
2. 国网江苏省电力有限公司电力科学研究院, 江苏 南京 211103
电力系统运行发展过程中, 输电线路一直受到外绝缘闪络的影响。污秽闪络是电力系统外绝缘的主要威胁之一, 其显著特点是同时多点跳闸几率高。绝缘等级越低, 跳闸几率越高, 且重合闸成功率小[1-3]。输电线路外绝缘的积污水平显著影响线路的绝缘水平, 在特殊工业粉尘地区, 大气污秽问题越发严重, 且由于污秽成分的特殊性, 使得该区域外绝缘闪络风险显著增加[4-7]。
现有输电线路绝缘子积污特性分析大多通过现场测量污秽的盐密和灰密(non soluble deposit density, NSDD), 按照气候和环境条件模拟计算污秽水平[8-15]。但此类方法未考虑特殊地区污秽的特殊性, 忽略了污秽中特殊成分对输电线路绝缘水平的影响[16-22]。在某些特殊重工业区、化工区, 工业粉尘成分复杂, 其中含有较大比例的铁粉及铜粉等金属微粒、碳粉等导电性微粒、糖分等吸水性物质、硫化物等酸性腐蚀性成分, 该类工业粉尘对电力设备污闪性能影响较大。运行于该种特殊粉尘污秽条件下的复合绝缘子, 表面更容易染污、吸水, 进而在极端运行条件下产生局部爬电, 对硅橡胶形成烧蚀或酸、碱性腐蚀, 极大影响绝缘子的电气性能。
文中对特殊工业粉尘地区运行的复合绝缘子自然积污特性进行研究, 通过离子色谱(ion chromatography, IC)、电感耦合等离子体发射光谱仪(inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometer, ICP)和X射线光电子能谱(X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, XPS)分析等手段分析绝缘子表面污秽可溶盐成分、惰性污秽颗粒成分。基于分析结果, 结合地区特性, 对特殊工业粉尘地区复合绝缘子的积污特性进行评估, 为线路外绝缘防污的工作奠定理论基础。
1 污秽特性分析为分析特殊工业粉尘地区输电线路复合绝缘子积污特性, 选取江苏某特殊工业园区运行复合绝缘子进行采样与测试。选取具有典型特点的4支复合绝缘子进行检测, 绝缘子样品型号均为FXBW-220/120, 运行年限为5 a, 运行地点周围有严重的化工污染, 绝缘子表面存在明显可见的自然污秽。
通过洗刷法对绝缘子表面的污秽进行取样, 并对污秽成分进行检测, 污秽成分分析方法见图 1。

|
图 1 绝缘子污秽成分分析方法 Fig. 1 Analysis method of insulator dust ingredients |
分析内容为复合绝缘子表面污秽盐灰密测试、污秽可溶盐成分分析、污秽不溶物成分分析。绝缘子污秽度检测参照GB/T 26218.1—2010进行, 计算等值盐密(equivalent salt deposit density, ESDD)、NSDD分别表征污秽中可溶盐和难溶灰分含量。使用ICP和IC等工具, 分析污秽可溶盐成分中的阴、阳离子组成及浓度。使用XPS分析惰性不溶物成分。基于上述检测方法得到该地区复合绝缘子污秽的主要成分, 进而对特殊工业粉尘地区复合绝缘子自然积污特性进行分析。
2 试验结果与分析 2.1 ESDD和NSDD参照标准GB/T 26218.1—2010, 使用去离子水擦洗绝缘子表面污秽, 对所得污液进行ESDD和NSDD测算, 评估其表面污秽度, 检测结果见表 1。
|
|
表 1 ESDD和NSDD检测结果 Table 1 Test results of ESDD and NSDD |
由表 1可知, 所述4支典型绝缘子中, ESDD平均为0.1~0.2 mg/cm2, 盐灰比为1 :2~1 :1, 说明该特殊工业粉尘污秽地区, 污秽中的含盐量较高, 相对含灰量较低。分布在绝缘子表面的污秽, 肉眼可见的主要成分为灰分及其他不溶成分。因此, 在该批绝缘子中, 直接观测污秽度不明显的样品, 其表面ESDD仍可能处于较高水平, 在潮湿情况下将会较大程度削弱绝缘子表面的绝缘性能。
2.2 可溶盐成分绝缘子表面污秽可溶盐成分检测结果如表 2、表 3所示。对离子的摩尔分数进行计算, 用对应离子浓度求出样品中含该离子的物质的量, 再根据不同离子在总样品离子中物质的量的占比, 分别求出阴、阳离子的摩尔分数x。
|
|
表 2 阳离子摩尔分数 Table 2 Mole fraction of cation |
|
|
表 3 阴离子摩尔分数 Table 3 Mole fraction of anion |
由表 2、表 3可知, 样品污秽可溶盐成分中的阳离子成分相近, 均以Ca2+为主, 占比均约为80%, Na+均约为10%, 其他离子成分占比均小于10%。而各样品中污秽成分的阴离子存在一定差异, 其中1, 2号样品F-含量较高, 占比为35%~50%, NO3-含量较低, 均低于5%;3, 4号样品F-含量为10%~20%, NO3-含量相对较高; 4份样品的SO42-含量相近。可以看出, 4份样品中主要盐成分较为相近, 均为硫酸钙(CaSO4), 其中1, 2号样品的F-离子含量较高。
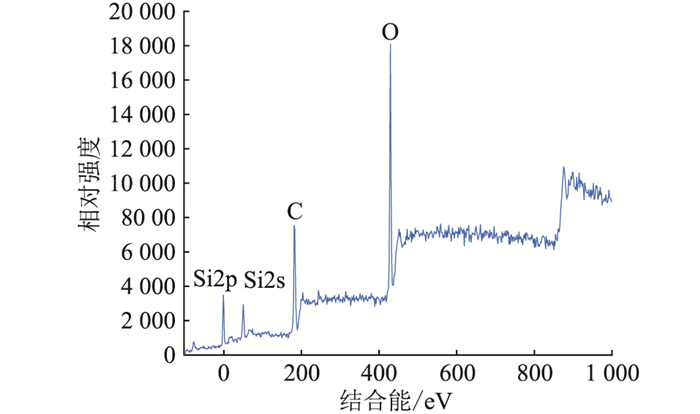
2.3 XPS结果分析对污秽过滤后的不溶物进行采样, 并进行XPS分析, 得到复合绝缘子样品表面污秽的元素组成和含量。由于该种惰性物质的主要成分尚不明确, 因此先对污秽成分进行整体全谱分析。在确认相应的污秽大致元素后, 对所测得的结果进一步分析对应侧谱, 测试相应元素的价态情况及化合物存在形态。XPS分析的各元素成分对应的结合能及其相对强度如图 2所示。
|
图 2 XPS谱图 Fig. 2 XPS spectrogram |
由图 2可知, 污秽的主要成分为碳(C)、氧(O)、硅(Si)3种元素。根据Si原子核外电子的排布特性可知, 离原子核较近的电子具有较低的能量, 随着电子层数的增加, 电子的能量越来越大。同一层中, 各亚层的能量按s, p, d, f的次序增强, 电子在原子核外排布时遵守1s, 2s, 2p排列。因此Si原子在XPS谱图中表现出Si2s、Si2p 2种化学态, 分别表征Si原子2种不同的最外层电子排布情况。在考虑污秽中Si元素成分时, 2种化学态均应纳入考虑。分别对4个样品的XPS谱图进行分析, 得到不溶物的主要元素及其占比, 如表 4所示。
|
|
表 4 污秽不溶物的主要元素及其相对含量 Table 4 The main elements and their relative contents of dust insoluble matter |
由表 4可知, 污秽不溶物主要元素为10%左右的Si, 40%左右的O, 50%左右的C。其中1, 2号样品中C元素含量较高、O元素含量较低, 4份样品中的Si元素成分都较为相近。可以推测污秽中的不溶物成分包含二氧化硅(SiO2)、碳粉等成分。
3 分析与讨论在特殊工业粉尘地区, 污秽会快速从空气中沉降并附着到绝缘子表面, 经过一个积污期, 绝大部分样品的ESDD都超过0.1 mg/cm2, 污秽度较高。而测量结果表明, 样品表面盐灰量较低, 因此样品表面可视污秽程度不高。
进一步分析自然污秽中的可溶盐成分可知, 污秽可溶物阳离子中的Ca2+, Na+, K+, Mg2+比例较突出。通过对阴、阳离子含量进行配比分析可知:可溶盐主要成分为CaSO4, 考虑到污秽中阴离子成分主要为SO42-, 3种阳离子对应的盐分别是硫酸钠(Na2SO4)、硫酸钾(K2SO4)和硫酸镁(MgSO4), 同时包含一定量的氯化钠(NaCl)、氟化钙(CaF2)。
污秽的不溶惰性成分中, 主要元素含量为C, Si, O, 说明污秽中的灰分主要包含SiO2、碳粉等物质, 以及包含部分可溶、微溶于水的氧化物如氧化钙(CaO)等, 同时存在一定量的糖类, 如(CH2O)n等物质。
4 结论以特殊工业粉尘地区运行的复合绝缘子为研究对象, 研究典型工业粉尘环境中复合绝缘子的积污特性, 得出的结论为:
(1) 采用ESDD、NSDD测量判断绝缘子表面染污程度, 进一步使用微观分析对特殊污秽可溶物、不溶物成分进行分析, 可定性得到特殊工业粉尘地区的复合绝缘子积污特性, 且效果较佳。
(2) 特殊工业粉尘环境中污秽自由沉降作用明显, 绝缘子表面污秽度普遍较重, 污秽的ESDD数值偏高, 盐灰比数值较低。污秽中含有数量较大的盐分, 而灰分较低, 绝缘子表面直观污秽并不明显。
(3) 特殊工业粉尘环境中, 绝缘子污秽可溶盐成分主要为微溶的二价盐CaSO4, 复合绝缘子污秽中Na2SO4, K2SO4, MgSO4比例较为明显。自然污秽的不溶物灰分主要元素为C, O, Si, 含碳粉、二氧化硅(SiO2)、氧化钙、糖类等物质。
(4) 特殊工业粉尘地区污秽中的不溶物影响复合绝缘子表面的导电性及吸水性, 从而影响绝复合绝缘子的绝缘性能。该部分不溶物是特殊工业粉尘地区的绝缘子在使用传统污秽度评价方法时, 与其他地区结果存在差异的主要原因。
| [1] |
刘世涛, 李秀广, 李焕友, 等. 高污秽度环境中绝缘子积污特性研究[J]. 绝缘材料, 2019, 52(1): 63-67. LIU Shitao, LI Xiuguang, LI Huanyou, et al. Research on contamination accumulation characteristic of insulators in heavy polluted environment[J]. Insulating Materials, 2019, 52(1): 63-67. (  0) 0) |
| [2] |
薛兵, 牟霖, 袁小清, 等. 双伞瓷绝缘子表面冶金污秽的积污特性及成分研究[J]. 绝缘材料, 2019, 52(4): 75-80. XUE Bing, MOU Lin, YUAN Xiaoqing, et al. Study on accumulation characteristics and composition of metallurgical contamination on porcelain insulator surface[J]. Insulating Materials, 2019, 52(4): 75-80. (  0) 0) |
| [3] |
廖一帆, 杨宇轩, 张福增, 等. 南方电网沿海绝缘子积污成分与海洋盐雾及附近污染源的关联性[J]. 电瓷避雷器, 2018(5): 191-196, 201. LIAO Yifan, YANG Yuxuan, ZHANG Fuzeng, et al. The correlation between the pollution components of coastal insulators in the CSG and the salt fog and the nearby pollution sources[J]. Insulators and Surge Arresters, 2018(5): 191-196, 201. (  0) 0) |
| [4] |
李恒真, 刘刚, 李立浧. 绝缘子表面自然污秽成分分析及其研究展望[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31(16): 128-137. LI Hengzhen, LIU Gang, LI Licheng. The analysis and research prospect of natural contamination composition oninsulator surface[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31(16): 128-137. (  0) 0) |
| [5] |
SULAIMAN A E, QURESHI M I. Effect of contaminationon the leakage current of inland desert insulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electrical Insulation, 1984, 19(4): 332-339. (  0) 0) |
| [6] |
RAMOS N G, CAMPILLO R M T. A study on the characteristics of various conductive contaminants accumulated on high voltage insulators[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1993, 8(4): 1842-1850. DOI:10.1109/61.248293 (  0) 0) |
| [7] |
张志劲, 张东东, 袁超, 等. 污秽成分对XP-160绝缘子串交流闪络特性的影响[J]. 高电压技术, 2014, 40(7): 1970-1976. ZHANG Zhijin, ZHANG Dongdong, YUAN Chao, et al. The effect of pollution composition on AC flashover performance of XP-160 insulator strings[J]. High Voltage Technology, 2014, 40(7): 1970-1976. (  0) 0) |
| [8] |
梅红伟, 毛颖科, 卞星明, 等. 相对湿度对绝缘子泄漏电流最大值的影响[J]. 高电压技术, 2010, 36(3): 627-631. MEI Hongwei, MAO Yingke, BIAN Xingming, et al. The influence of relative humidity on the maximum leakage current of insulators[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2010, 36(3): 627-631. (  0) 0) |
| [9] |
宿志一. 用饱和盐密确定污秽等级及绘制污区分布图的探讨[J]. 电网技术, 2004(8): 16-19. SU Zhiyi. Study on defining pollution classes and mapping pollution areas with saturated salt[J]. Power System Technology, 2004(8): 16-19. (  0) 0) |
| [10] |
谷裕, 郝艳捧, 张福增, 等. 沿海地区与内陆地区复合支柱绝缘子直流污闪特性比较[J]. 电网技术, 2014, 38(5): 1373-1378. GU Yu, HAO Yanpeng, ZHANG Fuzeng, et al. Comparison of DC flashover characteristics of composite insulators in coastal areas and inland areas[J]. Power System Technology, 2014, 38(5): 1373-1378. (  0) 0) |
| [11] |
高峰, 李瑶琴, 李黎, 等. 哈郑线河南段带电绝缘子污秽成分及悬挂高度对积污的影响[J]. 电网技术, 2015, 39(10): 2923-2928. GAO Feng, LI Yaoqin, LI Li, et al. Analysis on contamination components of energized insulator of Hami-Zhengzhou overhead line in Henan and influence of installation height on pollution accumulation[J]. Power System Technology, 2015, 39(10): 2923-2928. (  0) 0) |
| [12] |
刘嵘, 张燕, 段玉兵, 等. 山东电网绝缘子表面污秽成分特点分析[J]. 电瓷避雷器, 2017, 278(4): 209-214. LIU Rong, ZHANG Yan, DUAN Yubing, et al. Analysis on the characteristics of surface contamintiaon composition of insulators in Shandong power grid[J]. Insulators and Surge Arresters, 2017, 278(4): 209-214. (  0) 0) |
| [13] |
胡文堂, 王少华, 姜文东, 等. 基于污闪电压的自然积污绝缘子外绝缘状态评价[J]. 浙江电力, 2016, 35(3): 1-3. HU Wentang, WANG Shaohua, JIANG Wendong, et al. External insulation condition evaluation of naturally polluted insulators based on pollution flashover voltage[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2016, 35(3): 1-3. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-1881.2016.03.001 (  0) 0) |
| [14] |
蒋兴良, 舒立春, 孙才新. 电力系统污秽与覆冰绝缘[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2009. JIANG Xingliang, SHU Lichun, SUN Caixin. Power system pollution and icing insulation[M]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2009. (  0) 0) |
| [15] |
刘贞瑶, 叶辉. 应用饱和盐密原理修订江苏电网污区分布图[J]. 华东电力, 2008, 36(8): 51-54. LIU Zhenyao, YE Hui. Modifying pollution plots of Jiangsu power grid by using saturated equal salt deposit density[J]. East China Electric Power, 2008, 36(8): 51-54. (  0) 0) |
| [16] |
肖嵘.华东电网输电线路绝缘子饱和污秽(盐密)特性及外绝缘配置方法的研究[D].上海: 上海交通大学, 2009. XIAO Rong. Study on east China grid transmission line insu- lator saturated contamination(salt density) the characteristic and outside insulates configuration method[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2009. (  0) 0) |
| [17] |
张福增, 赵锋, 杨皓麟, 等. 高海拔直流线路大吨位绝缘子配置方法研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2008, 297(34): 21-26. ZHANG Fuzeng, ZHAO Feng, YANG Haolin, et al. Design method of outdoor insulation for DC transmission lines at high altitudes[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2008, 297(34): 21-26. (  0) 0) |
| [18] |
卢明, 李瑶琴, 李黎, 等. 哈郑特高压直流负极线路上U70BL型绝缘子自然积污规律[J]. 高电压技术, 2016, 42(2): 557-563. LU Ming, LI Yaoqin, LI Li, et al. Natural contamination deposit law of U70BL type insulators of Hami-Zhengzhou UHVDC negative line[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2016, 42(2): 557-563. (  0) 0) |
| [19] |
孙保强, 王黎明, 关志成, 等. 电压种类及极性对绝缘子积污的影响[J]. 高电压技术, 2013, 39(12): 3101-3108. SUN Baoqiang, WANG Liming, GUAN Zhicheng, et al. Influence of voltage types and polarity on contamination of insulators[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2013, 39(12): 3101-3108. (  0) 0) |
| [20] |
蔡炜, 肖勇, 吴光亚. ±500 kV直流线路绝缘子串自然积污规律初探[J]. 高电压技术, 2003, 29(6): 4, 40. CAI Wei, XIAO Yong, WU Guangya. Elementary analysis of pollution rules of insulators on ±500 kV DC transmission lines[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2003, 29(6): 4, 40. (  0) 0) |
| [21] |
曹燕明, 马为民. 特高压直流绝缘子的污秽测量技术[J]. 高电压技术, 2007, 33(1): 22-25. CAO Yanming, MA Weimin. Pollution measurement technology of insulators for UHVDC[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2007, 33(1): 22-25. (  0) 0) |
| [22] |
李恒真, 刘刚, 李立浧. 自然污秽成分CaSO4对电力设备外绝缘沿面绝缘特性的影响综述[J]. 电网技术, 2011, 35(3): 140-145. LI Hengzhen, LIU Gang, LI Licheng. A review on influence of natural contaminant CaSO4 on surface insulation characteristics of external insulation of power equipment[J]. Power System Technology, 2011, 35(3): 140-145. (  0) 0) |
2. State Grid Jiangsu Electric Power Co., Ltd. Research Institute, Nanjing 211103, China
 2021, Vol. 40
2021, Vol. 40


 邵仕超(1996), 男, 硕士在读, 研究方向为绝缘子污秽闪络(E-mail:
邵仕超(1996), 男, 硕士在读, 研究方向为绝缘子污秽闪络(E-mail: